Peritoneal Dialysis
What is Peritoneal Dialysis?
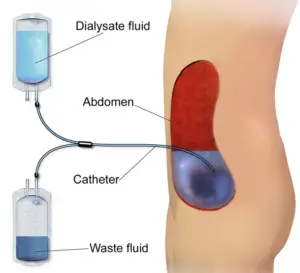
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a type of dialysis used to treat kidney failure. It’s a process that uses the lining of your abdomen (peritoneum) and a solution called dialysate to remove waste products and extra fluid from your blood.
There are different types of peritoneal dialysis, including continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD). In CAPD, manual exchanges of dialysate are done several times throughout the day, while in APD, a machine called a cycler performs the exchanges automatically while the patient sleeps.
What happens during Peritoneal Dialysis?
During peritoneal dialysis, a sterile solution containing minerals and glucose is introduced into your abdomen through a catheter. The peritoneal membrane acts as a filter, allowing waste products and excess fluid to pass from your blood into the dialysate. After a period of time, the used dialysate along with the waste products and excess fluid is drained from your abdomen, completing one cycle of peritoneal dialysis.
Why Choose peritoneal dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is chosen by many individuals as their preferred method of kidney replacement therapy due to its lifestyle flexibility, fewer dietary restrictions compared to hemodialysis, and potential preservation of residual kidney function. PD also eliminates the need for vascular access, reducing the risk of associated complications like infections and clotting. Its continuous therapy nature may be advantageous for patients who cannot tolerate the fluid and electrolyte fluctuations of intermittent hemodialysis.
Furthermore, PD allows patients to take an active role in managing their treatment, fostering a sense of empowerment and independence. This modality may be particularly suitable for patients with limited vascular access options or a history of vascular access complications. Ultimately, the decision to choose PD over other dialysis options is influenced by individual patient factors, preferences, and lifestyle considerations, and should be made in consultation with healthcare providers.
What are the benefits of Peritoneal Dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis offers several benefits for individuals with kidney failure:
- Lifestyle Preservation: PD preserves residual kidney function better than hemodialysis for some patients, potentially leading to better long-term outcomes and a higher quality of life.
- Fewer Dietary Restrictions: PD imposes fewer dietary restrictions compared to hemodialysis, allowing patients to enjoy a more varied diet and potentially improving their overall well-being.
- Vascular Access: PD does not require the creation of vascular access, reducing the risk of complications associated with access sites such as infections, clotting, and stenosis.
- Continuous Therapy: PD provides continuous therapy, which may be beneficial for patients who are unable to tolerate fluctuations in fluid and electrolyte levels that occur with intermittent hemodialysis treatments.
- Preservation of Residual Renal Function: Some evidence suggests that PD may better preserve residual kidney function compared to hemodialysis, potentially leading to better long-term outcomes for some patients.
- Suitable for Patients with Vascular Access Issues: PD may be a preferred option for patients with limited vascular access options or a history of vascular access complications.
Peritoneal dialysis serves as an effective treatment option for individuals experiencing kidney failure. By utilizing the peritoneal membrane and dialysate solution to remove waste products and excess fluid from the blood, PD offers various advantages over hemodialysis. Its flexibility, fewer dietary restrictions, and potential preservation of residual kidney function contribute to improved lifestyle preservation and overall well-being for patients. Moreover, PD eliminates the need for vascular access, reduces the risk of associated complications, and provides continuous therapy, making it a suitable choice for individuals with vascular access issues or those who require consistent treatment. Ultimately, the decision to choose PD as a preferred dialysis modality should be carefully considered in consultation with healthcare providers, taking into account individual patient factors, preferences, and lifestyle considerations.