Apheresis
What is Apheresis?
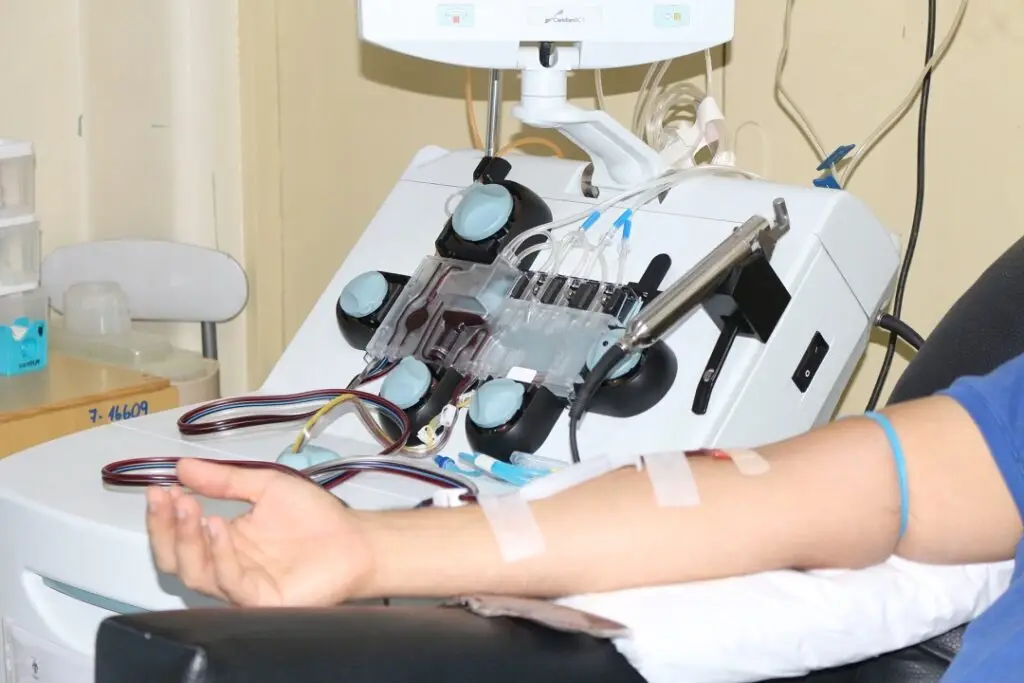
Apheresis, also known as therapeutic apheresis or plasmapheresis, is a medical procedure that involves removing blood from a patient, separating specific components such as plasma or cells, and returning the remaining blood components back to the patient. This process allows for the selective removal or collection of certain substances from the blood, such as plasma, platelets, white blood cells, or red blood cells, depending on the medical condition being treated. Apheresis is used in various therapeutic settings to treat conditions such as autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, certain types of cancer, and to collect specific blood components for transfusion purposes.
How long does Apheresis take?
The duration of apheresis can vary depending on the specific treatment protocol and the patient’s condition. Some apheresis procedures may take several hours to complete, while others may be shorter. Throughout the procedure, patients are closely monitored by our nursing staff to ensure their safety and comfort.
After the apheresis procedure is completed, patients may experience temporary side effects such as dizziness, lightheadedness, or bruising at the needle insertion site. However, these side effects are usually mild and resolve quickly.
What conditions require apheresis?
Apheresis is utilized to treat various medical conditions by selectively removing or collecting specific components from the blood. Apheresis is employed in the treatment of autoimmune disorders like Guillain-Barré syndrome, myasthenia gravis, and rheumatoid arthritis, by eliminating harmful antibodies or immune complexes from the blood. It is also used in neurological disorders such as multiple sclerosis and chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy to remove antibodies or toxins associated with these conditions.
Additionally, apheresis is beneficial in hematological disorders like thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome, as well as in certain cancers where it can collect specific blood components for treatment purposes. Metabolic disorders like familial hypercholesterolemia and porphyria, as well as conditions requiring organ transplantation, may also benefit from apheresis by removing harmful substances or antibodies from the blood. Overall, apheresis serves as a versatile therapeutic procedure with applications across a wide range of medical conditions, providing targeted treatment by manipulating blood components to achieve therapeutic goals and improve patient outcomes.
What are the benefits of Apheresis?
There are several benefits associated with apheresis:
- Selective Removal of Substances: Apheresis allows for the selective removal of specific substances from the blood, such as harmful antibodies, immune complexes, toxins, or excess blood components. This targeted removal can be beneficial in treating various medical conditions by reducing the levels of harmful substances in the bloodstream.
- Treatment of Specific Medical Conditions: Apheresis is used to treat a wide range of medical conditions, including autoimmune disorders, neurological disorders, hematological disorders, metabolic disorders, and certain types of cancer. By removing or collecting specific blood components, apheresis can help manage symptoms, improve outcomes, and potentially halt disease progression.
- Immediate Relief of Symptoms: In some cases, apheresis can provide immediate relief of symptoms by rapidly removing harmful substances from the bloodstream. This can be particularly beneficial in acute conditions or during disease flares when prompt intervention is needed.
- Reduced Dependence on Medications: For certain conditions, apheresis may reduce the need for long-term medication use by effectively removing disease-causing substances from the blood. This can lead to improved quality of life for patients and may reduce the risk of medication-related side effects.
- Improved Transplant Outcomes: In transplant recipients, apheresis can help prevent organ rejection by removing antibodies that could target the transplanted organ. This can improve transplant outcomes and increase the likelihood of long-term graft survival.
- Customized Treatment Approach: Apheresis treatments can be tailored to each patient’s specific needs and medical condition. This customization allows our team to optimize treatment outcomes while minimizing potential risks and side effects.
Apheresis is a vital medical procedure that allows for the selective removal or collection of specific components from the blood to treat various medical conditions. By utilizing specialized machines and under the supervision of trained medical professionals, apheresis can effectively target and manage conditions such as autoimmune diseases, neurological disorders, hematological disorders, metabolic disorders, and certain types of cancer. The duration of apheresis varies depending on the treatment protocol and the patient’s condition, and while temporary side effects such as dizziness or bruising may occur, the procedure is generally well-tolerated. Overall, apheresis serves as a versatile therapeutic procedure with wide-ranging applications, providing targeted treatment to improve patient outcomes across a diverse array of medical conditions.